Вивчення англійської мови може бути простим і захопливим, якщо підібрати відповідні матеріали та комфортний темп. На цьому сайті зібрані адаптовані тексти англійською, статті для читання та онлайн вправи, які підлаштовуються під рівень знань.
Тут можна почати англійську для початківців або навіть з нуля — усе повністю безкоштовно і доступно без реєстрації. Кожна стаття адаптована за рівнями (A1, A2, B1 і вище), щоб процес не перевантажував, а допомагав рухатися вперед і відчувати прогрес.
Для тих, хто хоче вивчити англійську мову самостійно, пропонуються різноманітні інструменти: читання англійською мовою онлайн, вправи з англійської граматики, практика англійської мови та тренажер англійських слів.
На сайті можна знайти англійські тексти з перекладом, щоб легше розуміти зміст нових слів, та англійські статті з різних тем — подорожі, робота, культура, повсякденне життя.
Якщо стоїть мета швидко вивчити англійські слова та покращити граматику англійської онлайн, підійдуть спеціальні інтерактивні завдання та рекомендації.
Для зручності є додаток для вивчення англійських слів та виразів, який нагадує про нові слова та допомагає закріплювати їх.
Усі матеріали створені так, щоб персоналізоване навчання англійській мові стало простим, доступним та результативним.
How to Make a Number Line for the Classroom
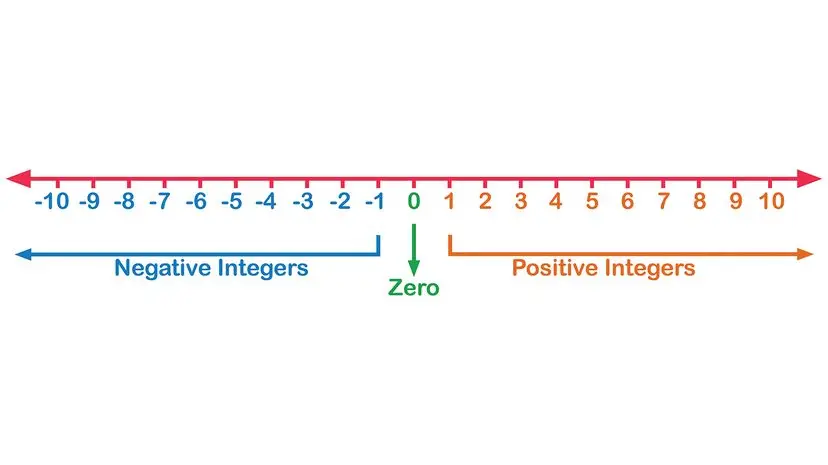
How to Create a Number Line for the Classroom
You can draw a number line to help students understand how numbers work. It's a visual tool to compare different types of numbers, like whole numbers, fractions, decimals, and even numbers like pi.
Here are some important rules to remember:
- Use a Straight Line: A number line should be a straight line, not a square or circle. This is because a number line shows a small part of a line that goes on forever in both directions.
- Negative Numbers on the Left: Numbers to the left of zero are negative. We mark them with points or small lines. For example, to the left of 0, you'll see -1, then -2, and so on. This helps show that subtracting a larger number from a smaller one gives a negative answer.
- Positive Numbers on the Right: Numbers to the right of zero are positive. These numbers grow as you move right. For example, to the right of 0, you'll see 1, then 2, and so on.
- Equal Spacing: All numbers on a number line should be the same distance apart. This equal spacing makes it easier to count or solve simple math problems. To do this, decide how many numbers you want to show. You can find the middle and count out from there, or measure the whole line and divide it by the number of values to find the right spacing.
A number line is usually a straight line with marks for each number. This is the simplest way to show numbers in order. You can choose any style that clearly helps students learn basic counting.
Interesting Math Fact
You can use dice to teach simple math. For example, students can subtract one roll from another. Also, if you look at a standard die, the numbers on opposite sides always add up to seven.
Navigating the World of Numbers Visually
Imagine a straight path that stretches endlessly in both directions – this is how we can picture numbers. This path, often used in classrooms, helps us understand where different numbers belong and how they relate to each other.
The Central Point: Zero
At the very heart of this number path is zero. It's the meeting point for two very different families of numbers.
Numbers to the Right: Growing Values
If you start at zero and move towards the right, you'll discover numbers that keep getting bigger. These are the familiar counting numbers (1, 2, 3...) and they show us how quantities increase. Think of them as steps forward on our infinite path.
Numbers to the Left: Decreasing Values
Moving from zero towards the left introduces us to numbers that are less than zero. These are often marked with a minus sign (-1, -2, -3...). They represent things like debt, temperatures below freezing, or moving backward. They show us how numbers can become smaller than nothing.
The Importance of Even Steps
For our number path to be truly useful, every step we take along it must be the same size. Whether we're moving from 0 to 1, or from -2 to -1, the distance between each number must be equal. This consistent spacing is key for learning to count, adding, and subtracting, as it correctly shows the true value and distance between any two numbers.
A Tool for Learning
This simple visual aid is invaluable for students. It makes abstract number concepts concrete, helping to build a strong foundation in mathematics. It shows not just what numbers are, but also how they behave and interact.
Fun Math Connection
Did you know that everyday items can hide interesting math facts? For instance, with a standard six-sided die, if you pick any two numbers on opposite faces and add them together, the total will always be seven. This little secret is built into how dice are made!
Вивчення англійської мови онлайн відкриває нові можливості для саморозвитку та кар’єри. Адаптовані статті та тексти допомагають поступово збільшувати словниковий запас і впевненість у використанні англійської.
Регулярне читання та виконання вправ роблять процес навчання звичкою, яка приносить результат. Чим частіше ви взаємодієте з англійською мовою, тим швидше помічаєте покращення.
Матеріали на сайті підходять як для початківців, так і для тих, хто продовжує вдосконалювати знання. Кожен може обрати зручний формат: читання, вправи, тренажери чи комбінацію всіх методів.
Англійська мова — це ключ до нових можливостей: подорожей, роботи за кордоном, доступу до світової інформації та спілкування без кордонів.
Почніть вчити англійську вже сьогодні — з простих адаптованих текстів та вправ. Поступово ви побачите прогрес, а навчання стане природною частиною вашого життя.